Measuring Angles using Protractor
A protractor is a tool used to measure and draw angles. The image below shows the essential parts of a protractor.
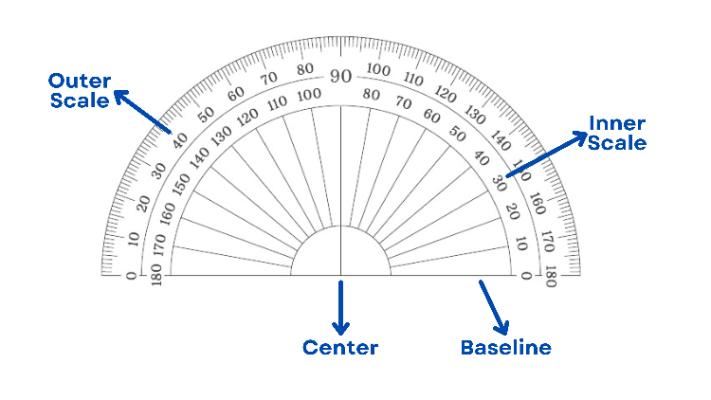
Parts of a Protractor
Center: The point at the very center of the semicircle.
Baseline: This is the straight line forming the flat bottom edge of the protractor. It serves as the base for aligning the protractor with the angle being measured.
Inner Scale: This scale also starts at 0° at the same endpoint but increases counter-clockwise until it reaches 180° at the other endpoint.
Outer Scale: This scale starts at 0° at one endpoint of the curved edge and increases clockwise until it reaches 180° at the other endpoint.
How to Measure an Angle using a Protractor
Step 1: Place the center of the protractor on the vertex of the angle.
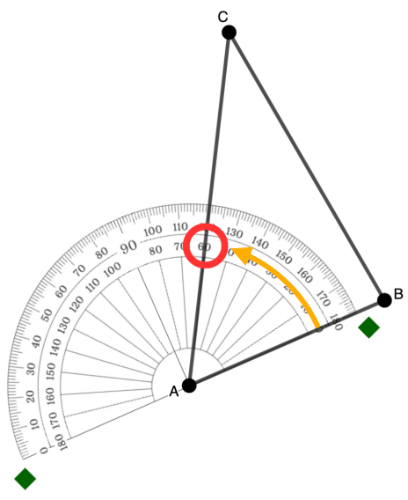
In the example below, to measure angle A, place the center of the protractor in point A.
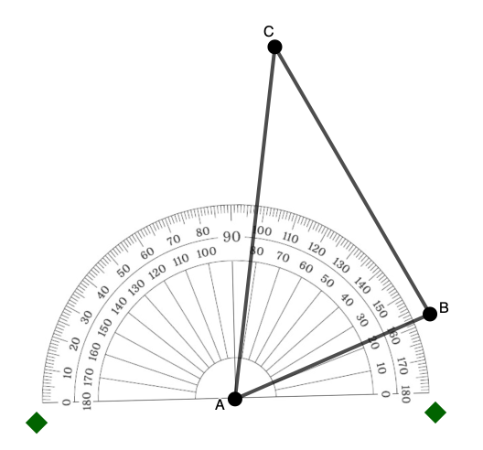
Step 2: Align the baseline of the protractor with one ray (side) of the angle.
In the example below, the baseline was aligned with side AB.
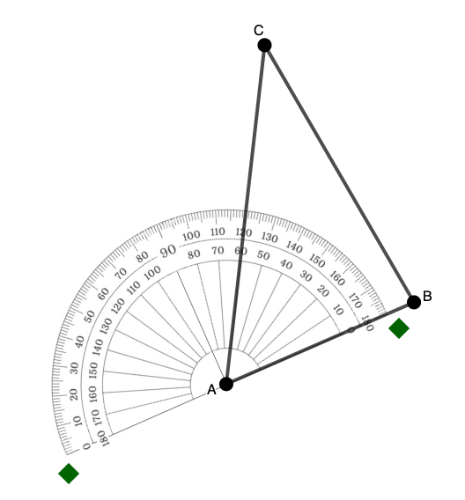
Step 3: Match the 0° mark on the appropriate scale of the protractor with the ray (or side) you aligned in step 2.
In the example below, the 0° mark where the ray is located is on the inner scale.
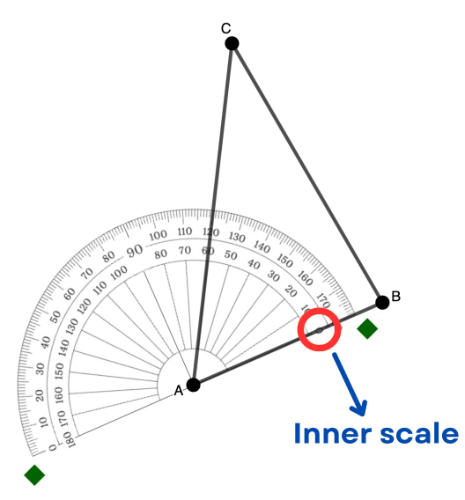
Step 4: Starting from the 0° mark, follow the rotation from the ray positioned in Steps 2 and 3 up to the other ray (or side) of the angle. The degree marking where the second side of the angle crosses the scale chosen in Step 3 is the angle measurement.
In the example below, from side AB rotating to the side AC, the side crosses the inner scale at 60°.
Thus, angle A has an angle measurement of 60°.
Practice: Measure the angles of the following polygons.
Drag the green points to move or rotate the protractor.
To display the polygon and the input box for your answers, click the checkbox. If the measurement entered for each angle is correct, a check mark will appear beside the input box.