Thales' Theorem
Brief historical context
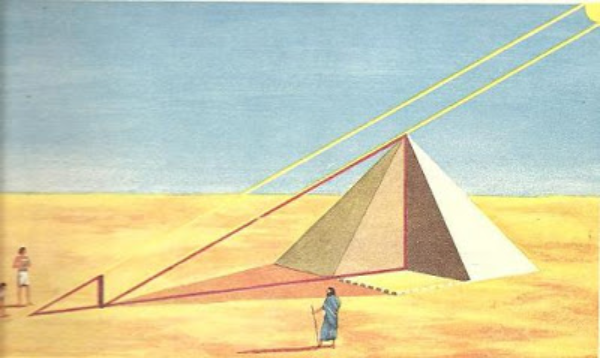
His wisdom reached many territories, going all the way to Egypt. So the Egyptians then invited him to measure the height of their pyramids, a great feat for the current period, as there was no type of equipment that could easily do so. Thales was able to measure the height of the pyramid using what we know today as the Thales Theorem. In order to devise this theorem he used the shadow caused by the sun and because of this process his reputation as a great mathematician and thinker, became even greater. (source: http://www.estudopratico.com.br/teorema-de-tales/)
Basic Definitions
Property
Analysis 1
Check the "Show / Hide Segment Measurements" box. Do segments AB, BC and CD have the same measure?
Analysis 2
Check the "Show / Hide Segment Measurements" box. Move points E, F and D so that the parallel lines are equidistant from each other. Do segments AB, BC and CD have the same measure? Justify your answer (if you need help, check the "Show / Hide Triangle" box)
Other property
Analysis 3
The following structure shows the corresponding segment being divided into fewer parts. Explain what is wrong in the previous statement.

Basic Concept
Analysis 4
Move points A, A', D or D' and observe the ratios. Do they change?