Circular motion 3d for IGCSE Physics
Task 1: [3 Marks]
- Start the simulation, and adjust the parameters (m: Mass, v: speed, F: centripetal force to values in the middle of their respective ranges. Your aim should get a value of the Radius between 0.75 and 1.00 m
- Note down the value of the radius.
- Now change EITHER the mass OR the speed of the moving body.
- Finally try to restore the radius noted in (2) above by adjusting the value of the required centripetal force F. (try to get a value of the Radius as close as possible to the initial value) This exercise will show what change in F is needed to maintain circular motion.
- Repeat steps 1 to 4 until you fully understand the relationship between the various parameters, then answer the questions below.
Q1 [1 Mark]
Complete the sentences by selecting the correct ending : (i) When a mass moves in a circle at a steady speed the centripetal force is larger if the :
Q2 [1 Mark]
When a mass moves in a circle at a steady speed the centripetal force is larger if the :
Q3 [1 Mark]
An apple is whirled round in a horizontal circle on the end of a string which is tied to the stalk. It is whirled faster and faster and at a certain speed the apple is torn from the stalk. Suggest reasons why ? [1 Mark]
Q4 [1 Mark]
A car rounding a bend travels in an arc of a circle. a) What provides the centripetal force?
Q5 [3 Mark]
b) Is a larger or a smaller centripetal force required if
Q6 : A girl swings a small mass on a rope around her head.
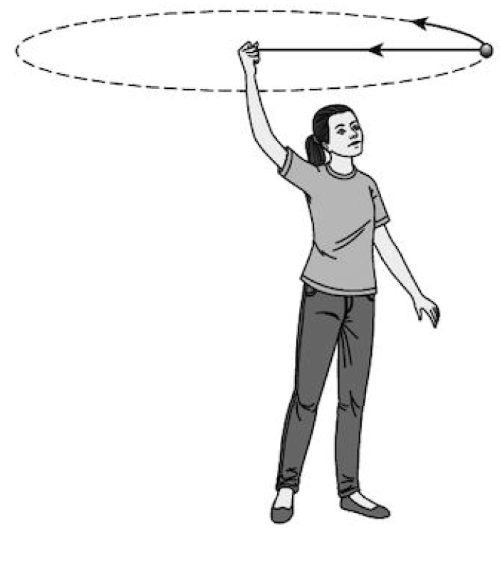
a. Which force provides the centripetal force? [1 Mark]
b. In which direction does this force act? [1 Mark]
c. What is the direction of the acceleration of the object [1 Mark]
d. Describe the motion of the object if the rope is cut [2 Mark]
Q6
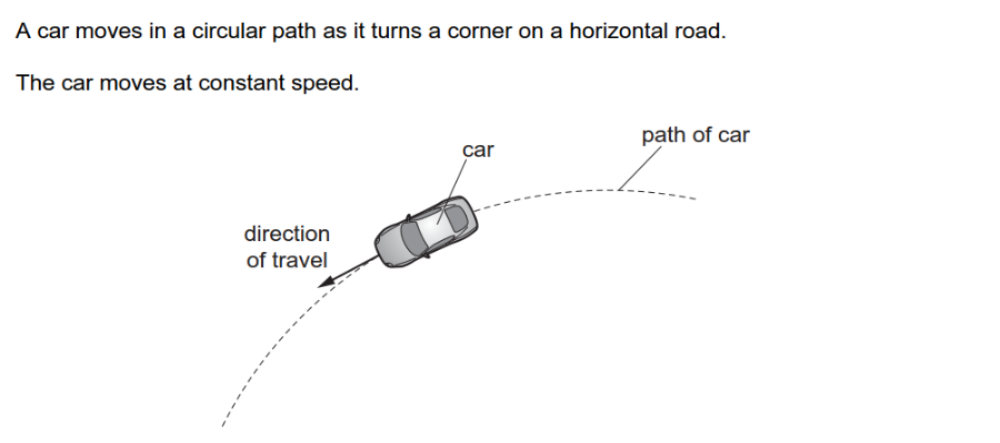
Which description of the forces acting on the car is correct? [1 Mark]
Q7: Fig 7.1 shows a model car moving clockwise around a horizontal circular track.
(a) A force acts on the car to keep it moving in a circle.
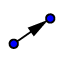 ) [2 Marks]
) [2 Marks]
(ii) The speed of the car increases. State what happens to the magnitude of this force. [1 Mark]
(b) The car travels too quickly and leaves the track at P.
(i) - On Fig. 7.1, draw an arrow to show the direction of travel after it has left the track. [1 Mark]
(ii) In terms of the forces acting on the car, suggest why it left the track at P. [2 Mark]
Q8: The Earth travels in a circular orbit around the Sun at constant speed.
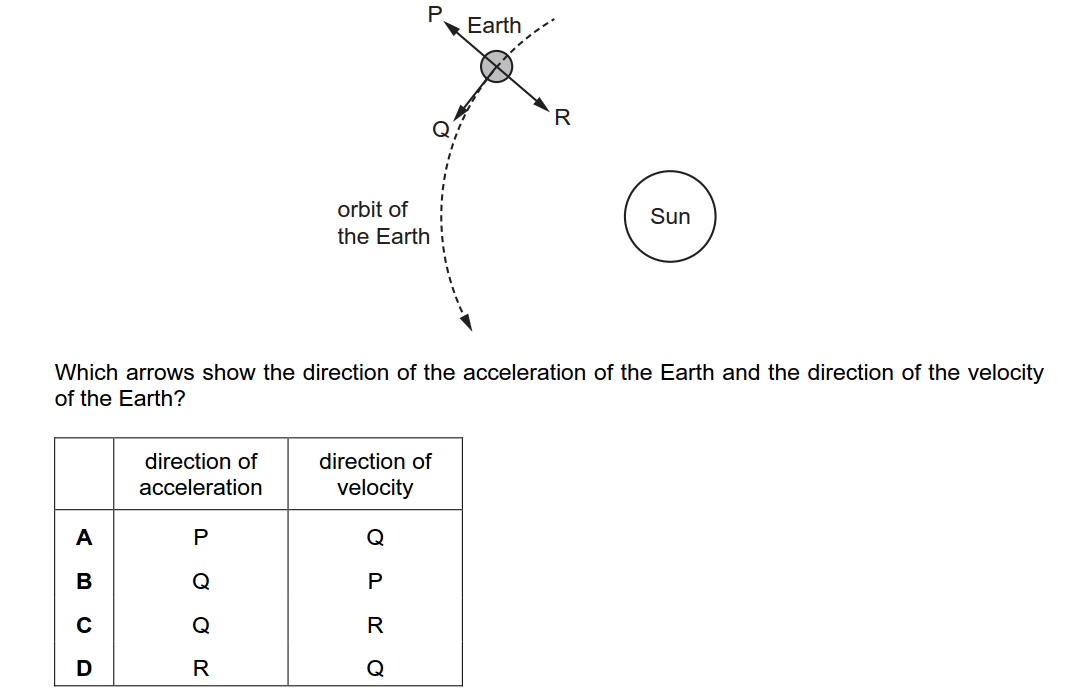
Your answer:A