How to Game Works...
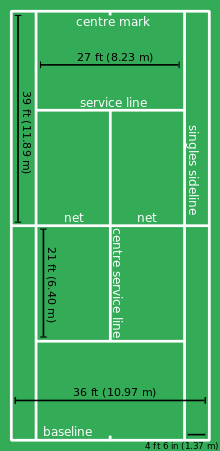
Tennis is played on a rectangular, flat surface. The court is 78 feet (23.77 m) long, and 27 feet (8.2 m) wide for singles matches and 36 ft (11 m) for doubles matches. Additional clear space around the court is required in order for players to reach overrun balls. A net is stretched across the full width of the court, parallel with the baselines, dividing it into two equal ends. It is held up by either a metal cable or cord that can be no more than 0.8 cm (1⁄3 in). The net is 3 feet 6 inches (1.07 m) high at the posts and 3 feet (0.91 m) high in the center. The net posts are 3 feet (0.91 m) outside the doubles court on each side or, for a singles net, 3 feet (0.91 m) outside the singles court on each side. The modern tennis court owes its design to Major Walter Clopton Wingfield. In 1873, Wingfield patented a court much the same as the current one for his stické tennis (sphairistike). This template was modified in 1875 to the court design that exists today, with markings similar to Wingfield's version, but with the hourglass shape of his court changed to a rectangle. Tennis is unusual in that it is played on a variety of surfaces. Grass, clay, and hardcourts of concrete or asphalt topped with acrylic are the most common. Occasionally carpet is used for indoor play, with hardwood flooring having been historically used. Artificial turf courts can also be found.
The dimensions of a tennis court