Modeling in AR
Task
Choose a real solid (cube, box, etc...) and create a model in GeoGebra 3D Calculator.
Watch this video...
Instructions
Choose the measurement tools to measure the length of the solids edges, the surface area, or the volume of your model.
| 1. | | Choose a real solid (like a cube, a tee box, etc...) and place it on your table. |
| 2. | | Open the GeoGebra 3D Calculator on your mobile device. |
| 3. | | Click on the AR button to switch to AR mode and follow the instructions on your device to detect a surface. |
| 4. |  | Go to the Tools View and make sure that the Move tool is selected. |
| 5. | | Have a look at the AR Ratio in the lower-left corner, which displays the ratio between the GeoGebra coordinate system and the real world. If the ratio is set to 1:1, you will later get the real dimensions of your model. |
| 6. | 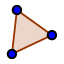 | Go to the Tools View, select the Polygon tool, and select each vertex of the base of the solid in a consecutive (clockwise or counterclockwise) order to create the base area. |
| | Hint: In the end you have to select the first point again to close the polygon. The more precise you set the points on the real object, the more precise your model becomes. | |
| 7. | 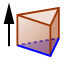 | Choose the Extrude to Prism tool and drag the polygon to the correct height. |
| 8. | 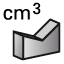 | Choose the Measure tools to measure the length of the edges, the surface or the volume of your model. |
| | | |
Additional Objects
You can create many different objects and place them around you as you walk around them. By using the AR Ratio, you can see the ratio between distance in the GeoGebra coordinate system to distance in the real world around you. Explore your constructions from a new perspective and compare virtual with real objects!