2) Conditional Probabilities
2) Conditional Probabilities
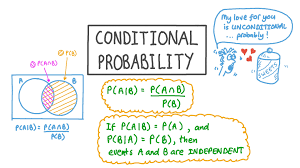
Conditional Probabilities P(A|B) or P(B|A)
Random Experiment: An experiment in which all possible outcomes are known, and the exact output cannot be determined in advance.
The conditional probability P(B|A) of an event B is the probability that the event will occur given an event A has already happened.
l
The conditional probability is calculated using the formula:
P(A|B) = P(A ∩ B) / P(B) or P(B|A) = P(A ∩ B) / P(A)
Questions students should be able to answer:
1) How is conditional probability different from finding the general probability of an event?
2) How to find the probability of an event given another event has happened?