Trigonometric Ratios
(Move the point labeled "Move" to adjust the dimensions of the triangle.)
(Move the point labeled "Move" to adjust the dimensions of the triangle.)
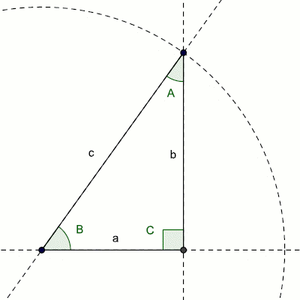
Sides of the right triangle:
Adjacent = a
Opposite = b
Hypoteneuse = c
Angles of the right triangle:
the angle opposite a = A
the angle opposite b = B
the angle opposite c = C
SOHCAHTOA:
SOH: Opposite / Hypoteneuse = sin(θ) = b / c
CAH: Adjacent / Hypoteneuse = cos(θ) = a / c
TOA: Opposite / Adjacent = tan(θ) = b / a
Hypoteneuse / Opposite = csc(θ) = c / b = 1 / sin(θ)
Hypoteneuse / Adjacent = sec(θ) = c / a = 1 / cos(θ)
Adjacent / Opposite = cot(θ) = a / b = 1 / tan(θ)
Other Functions:
1 = csc(θ)^2 - cot(θ)^2
1 = sec(θ)^2 - tan(θ)^2
1 = sin(θ)^2 + cos(θ)^2
1 = sec(θ) - exsec(θ)
1 = csc(θ) - coexsec(θ)
1 = vers(θ) + cos(θ)
1 = sin(θ) + covers(θ)
hav(θ) = vers(θ) / 2
Pythagorean Theorem:
c^2 = a^2 + b^2
Law of Sines:
2 * r = a / sin(A) = b / sin(B) = c / sin(C)
where "r" is the radius of the circumcircle
Law of Cosines:
cos(A) = (c^2 + b^2 - a^2) / (2 * b * c)
Law of Tangents:
(a + b) / (a - b) = tan((A + B) / 2) / tan((A - B) / 2)
Dot Product:
A · B = cos(θ) = xA * xB + yA * yB
where A and B are vectors with lengths equal to 1