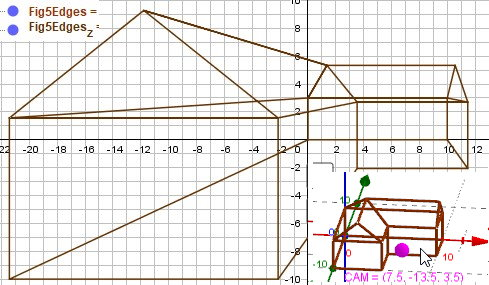
Cavalier-Cabinet-Central-Projection xy-z(Φ=45°,α=63.43°)
classic oblique projections
In classic oblique projections two coordinate axes are not changed by the mapping and a shearing is applied to the third.
The projection direction of the third axis is given by two angles α and Φ
The angle Φ is preserved in the projection and corresponds to the angle between the projected y- and x-axis. The angle α controls the ratio:
Cavalier projection x:y=1:1, α = Φ = 45°
Cabinet projection: x:y=2:1, α = 63.435° and Φ=45°
In classic mathematical theorem the y axis is vertical alined. here we use the school based coordinate system by z axis vertical (the projection was made for plane y=0, but plotted to plane z=0)!
Graphics Programming ( Torsten Thormählen)
Affine und projektive Räume (Oliver Deussen)
Grid models defined by Edges-varaibles
FignA - Pointlist 3D Figur
FignEdges - Polyline 3D Figur
FignEdges_V - Polygon 3D Figur
FignA_P - Pointlist 2D Projection Figur
FignEdges_P - Polyline 2D Projection Figur
FignEdges_Z - Polyline 2D Central Projection Figur
Making Figur 2 Pyramid (Tetrahedron) higher a/3->a/2

| | used projection matrix Standard projection matrix |
Oblique and Central Projection
Example Fig2A - Fig4A
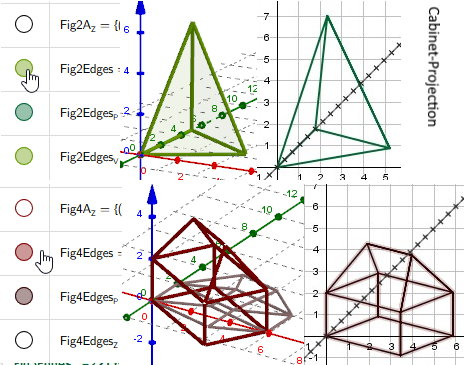
Fig3 Cabinet Projection
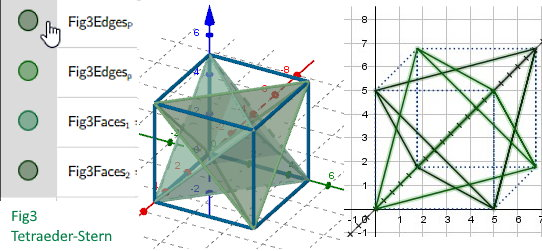
Fig4 central projection
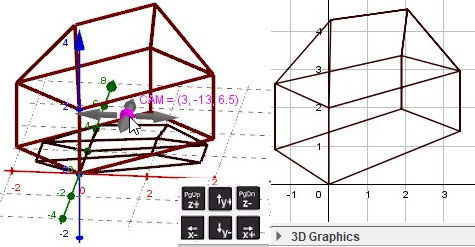
Fig5 Central Projection