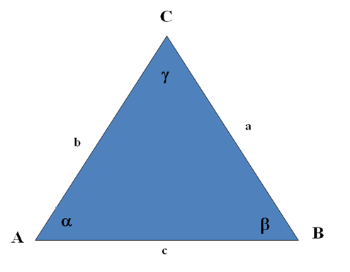
Triangles
Sum of all angles is 180°. The area of a triangle can be solved with the formula
where a is the base of the triangle and h is the perpendicular height of the triangle.
There are three special cases of triangles and all of them have features simplifying solving:
- equilateral triangle: all sides are equal and all angles are 60°.
- isosceles triangle: two sides of a triangle equal. Thus, base angles are also equal.
- right-angled triangle: one angle is 90°.