Visualizing integer addition
Task
Create a dynamic figure that visualizes the addition of integers on the number line.
Explore the construction...
Change the numbers of the blue and red sliders, in order to create new problems for adding integers on the number line.
Instructions
| 1. |  | Open the Settings of the  Graphics View using the Graphics View using the |
| 2. |  | On tab xAxis set the distance of tick marks to 1 by checking the box Distance and entering 1 into the text field. |
| 3. |  | On tab Basic set the minimum of the xAxis to -11 and the maximum to 11. |
| 4. |  | On tab yAxis uncheck Show yAxis and close the Settings. |
| 5. | 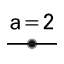
| Create two sliders a and b, both with Interval -5 to 5 and Increment 1. |
| 6. | 
| Show the value of the sliders instead of their names using the |
| 7. | 
| Create points A = (0 , 1) and B = A + (a , 0).
Hint: The distance of point B to point A is determined by slider a.
|
Try it yourself...
Instructions (continued)
| 8. | 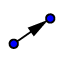
| Create a vector u = Vector(A, B) which has the length a.
|
| 9. | 
| Create points C = B + (0, 1) and D = C + (b, 0).
|
| 10. | 
| Create vector v = Vector(C, D) which has the length b.
|
| 11. | 
| Create point R = (x(D), 0).
Hint: The input x(D) gives you the x-coordinate of point D. Thus, point R shows the result of the addition on the number line.
|
| 12. |  | Create point Z = (0, 0).
|
| 13. | 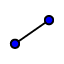
| Create three segments c = Segment(Z, A), d= Segment(B, C), and e = Segment(D, R).
|
| 14. | Use the Style Bar to enhance your construction (e.g. match the color of sliders and vectors, change line style, fix sliders, hide labels and points). |